MRI Room Testing
MRI Room Testing Solutions specializes in providing comprehensive testing services for MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) facilities. We ensure the safety, compliance, and efficiency of MRI rooms through thorough testing and analysis. Our team of certified technicians utilizes advanced equipment and industry-leading practices to deliver accurate results and recommendations.
At RADWRX, precise measurement and analysis of magnetic field strength to ensure it meets safety standards and minimizes risks.
We are committed to safeguarding the integrity and performance of MRI facilities, ensuring a safe and reliable environment for medical imaging procedures.
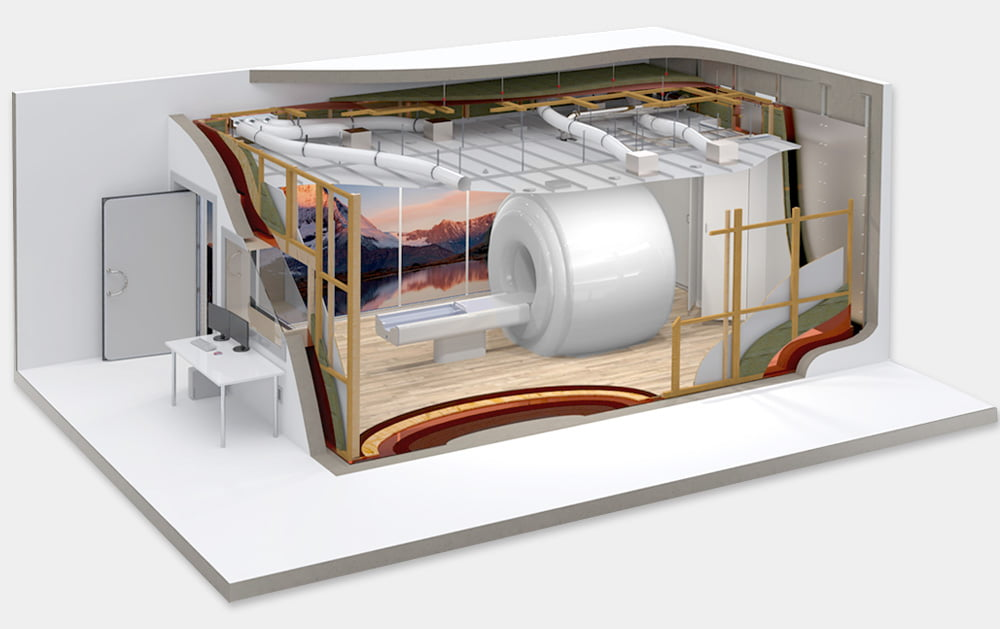
MRI ROOM TESTING
Our range of services covers all critical aspects of MRI room testing. From measuring magnetic field strength and assessing RF shielding integrity to evaluating gradient coil performance and detecting ferromagnetic objects, we leave no stone unturned in ensuring the safety and efficiency of MRI facilities. Furthermore, we meticulously analyze noise levels within MRI rooms, recognizing the importance of patient comfort and regulatory adherence. Our comprehensive reports offer detailed findings, actionable recommendations, and guidance on maintaining compliance and optimizing performance.
Electric currents that oscillate at radio frequencies have special properties not shared by direct current or alternating current of lower frequencies.

Radio Frequency (RF)
Applications: MRI, Cellular, Test Chambers, Specialty Rooms
Industry: Hospital, Laboratory, Government
Links: RF Products RF Services
Radio frequency (RF) is a rate of oscillation in the range of around 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals. RF usually refers to electrical rather than mechanical oscillations; however, mechanical RF systems do exist (see mechanical filter and RF MEMS).
Although radio frequency is a rate of oscillation, the term “radio frequency” or its abbreviation “RF” are also used as a synonym for radio – i.e. to describe the use of wireless communication, as opposed to communication via electric wires.